My Cart
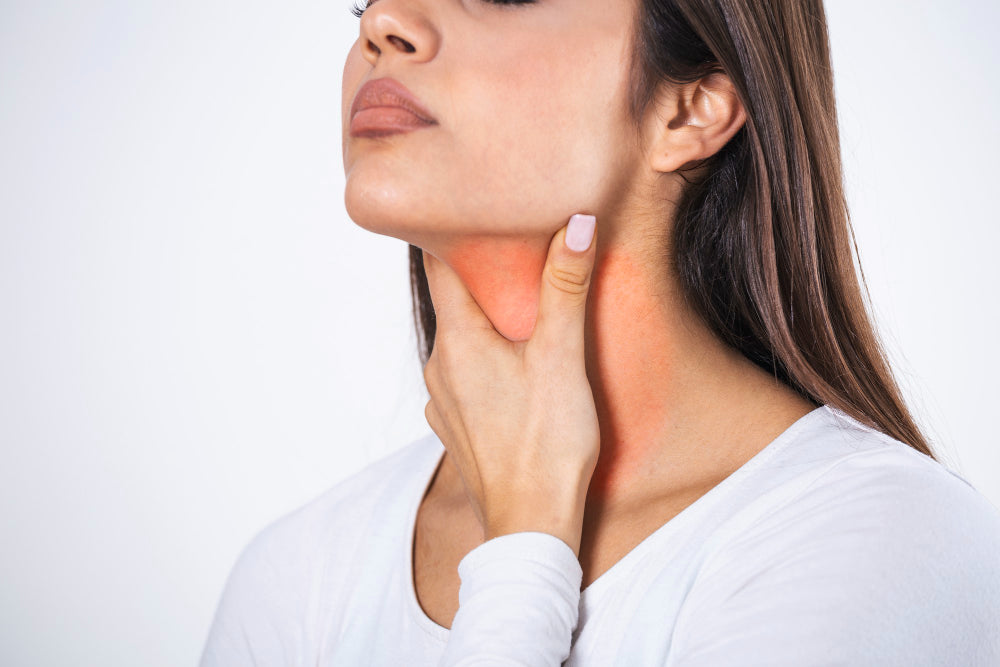
How Thyroid Impacts Your Sleep

Do you have difficulties falling asleep during the night? Do you experience fatigue despite getting a restful night’s sleep? Sleep is crucial for both physical and cognitive well-being. Recent studies have shown a link between sleep and thyroid diseases. In fact, people with thyroid disorders are two to four times more likely to experience sleep problems than people without thyroid diseases.
Some of the most common sleep issues associated with thyroid disease include difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, and transitioning from one sleep stage to another.
In this blog, we will discuss thyroid disease, its overall impact on sleep, and how to sleep better with the thyroid.
Common types and symptoms of thyroid disease

Thyroid disease refers to a condition that greatly affects the thyroid gland. A small gland in the neck region is called the thyroid gland. It regulates metabolism, pulse rate, and nearly every organ in the body. Thyroid disease can cause problems with your energy, weight, and mood.
There are two main types of thyroid disease: hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is the most common type of thyroid disease and is also known as an underactive thyroid. It refers to a reduced amount of thyroid hormone in your bloodstream. In its initial stages, hypothyroidism may not manifest any symptoms. However, untreated hypothyroidism can lead to other health problems, such as high cholesterol and heart problems, in the future.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism
Symptoms of hypothyroidism include:
- Exhaustion.
- Increased cold sensitivity.
- Depression.
- Constipation.
- Skin problems.
- Excessive weight.
- Face with puffiness.
- Hoarse voice.
- Hair problems.
- Weak muscles.
- Muscle pain, softness, and soreness.
- Irregular or heavier Menstrual cycles.
- Slowed pulse rate, also known as bradycardia.
- Memory Issues
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism arises when your thyroid gland creates an unusually higher quantity of thyroid hormone. Hyperthyroidism is also known as an overactive thyroid. It causes the body’s metabolism to accelerate. This can lead to a variety of ailments, including weight reduction, hand tremors, and a fast or erratic heartbeat.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism symptoms often look like other health problems, which makes it difficult to diagnose. A wide range of hyperthyroidism symptoms include:
- Irregular loss of weight.
- Tachycardia, or a rapid heartbeat.
- An arrhythmia or an irregular heartbeat.
- Palpitation or heart pounding.
- Increased appetite.
- Anxiety, distress, and mood swings.
- Tremors Changes in menstrual cycles.
- Sweating.
- Increased heat sensitivity.
- Changes in bowel patterns. A
- goiter or an enlarged thyroid gland.
- Fatigue.
- Muscle weakness.
- Sleeping difficulties.
- Skin and hair problems
What causes thyroid disease?

Thyroid disease can be caused by a number of factors, including genetics, age, and exposure to radiation or chemicals.
Sleep-wake cycle
Sleep deprivation is also associated with an increase in the occurrence of thyroid disease. Circadian rhythm disruption, a condition in which people’s natural body clocks are out of sync with their surroundings, has been linked to an increased risk of thyroid disease.
Additionally, thyroid cells produce hormones when they are active during the night and rest during the day. However, different sleep-wake cycles can disrupt this natural rhythm and lead to thyroid problems.
Autoimmune disorders
Thyroid dysfunction can also be caused by autoimmune disorders that attack the thyroid gland. It can occur as a result of an antigen (a foreign substance that triggers the immune system) present in the body’s tissues or as a problem with the autoimmune response itself. Thyroiditis, an autoimmune disorder that attacks the thyroid gland, is the most common type of autoimmune disorder.
Other causes of thyroid dysfunction include Hashimoto’s disease, Graves’ disease, and lupus erythematosus. Autoimmune disorders can also harm other organs in the body, such as the pancreas, lungs, and kidneys.
Lifestyle choices
Lifestyle choices can play a role in the development of thyroid disease. Smoking, being overweight, being inactive, and having high cholesterol are all associated with an increased risk of developing thyroid problems. Drinking alcohol also has adverse effects on thyroid function.
Furthermore, your sleeping pattern and regimen can make you more vulnerable to thyroid disease. For example, those who do not get enough sleep are at a higher risk of developing hyperthyroidism. On the other hand, those who sleep excessively may develop hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
Irregular food habits
Irregular food habits can be one of the causes of thyroid problems. When your body doesn’t get the right balance of nutrients, it could lead to an imbalance in the thyroid gland and eventually a thyroid problem.
Furthermore, iodine is an important mineral for thyroid function. It’s because the thyroid gland needs iodine to stimulate hormone production. Too little iodine can lead to abnormal thyroid hormone levels and eventually thyroid disease.
Pregnancy
One of the most common causes of thyroid problems is pregnancy. Women who are pregnant often have an increase in the hormones estrogen and progesterone, which can lead to an overproduction of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is required for the healthy development of both you and your baby. This can result in an increase in thyroid hormone production, which can cause symptoms such as weight gain, fatigue, and hair loss. That is why doctors pay close attention to hormonal changes in pregnant women. You should consider your hormonal changes during pregnancy, also you can buy mattress for pregnancy for better sleep also. In pregnancy restful sleep is necessary.
Who is at risk of developing a thyroid disorder?

Women are not the only ones who are at risk of developing a thyroid disorder. Anyone can develop thyroid dysfunction, even young men. The following are some of the people who are at risk:
1. Women: Approximately half of all cases of thyroid disorders occur in women. This is due to the fact that women have a higher concentration of thyroid hormones than men.
2.People who have a family history of thyroid disease: If you have a family history of thyroid disease, you are also at risk for developing it yourself.
3. People who have an autoimmune disorder: Autoimmune disorders are conditions in which the immune system attacks healthy tissue. Thyroid disorders can be caused by an autoimmune reaction against the thyroid.
4. People who take medications that suppress their immune systems: Some prescription and over-the-counter medications can suppress your immune system and lead to thyroid problems.
How does thyroid disease affect your sleep?

Thyroid issues may have a considerable effect on your sleep. The disorder can cause you to experience difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, and experiencing restless sleep. Toxic exposures, genetics, and age all play a role in how thyroid disease affects your sleep.
In general, people with thyroid disease are more susceptible to having disturbed sleep cycles. The thyroid hormone affects the body’s circadian rhythm, or the natural cycle of sleeping and waking, which helps regulate many biological processes. Reduced levels of thyroid hormone can disrupt the time-honoured process of falling asleep and staying asleep.
In some cases, people with thyroid disease may experience restless sleep and difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep through the night. Difficulties falling or staying asleep can be harmful to both mental and physiological health.
Hypothyroidism, or a lack of thyroid hormone, can have a significant impact on your sleep. In most cases, hypothyroidism makes it difficult to fall and stay asleep. People with hypothyroidism also tend to suffer from hypersomnia. This is when someone has an excessive amount of sleepiness during the day. They may find it difficult to remain awake for more than an hour or two at the same time. This can make it difficult to work or take care of your responsibilities.
Hyperthyroidism often causes difficulty sleeping through the night. People with hyperthyroidism may also experience restless legs syndrome, a condition in which people feel an irresistible urge to move their legs and often feel cold all over. Furthermore, people with hyperthyroidism may be more prone to depression or anxiety.
Additionally, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune condition that affects the thyroid gland, is associated with an increased risk of developing insomnia.
How to sleep better with thyroid disease?

So if you have a diagnosis of thyroid disease, paying close attention to your sleep habits is key to maintaining optimal health and reducing the risk of developing complications down the road. Here are some tips on getting a good night’s sleep:
Seek Treatment
Often, the wrong medications or not treating the thyroid can cause issues with sleeping. Therefore, the first and most crucial step towards improving sleep is to visit the doctor and get a proper diagnosis of your illness. When the root cause is addressed, it becomes easier to implement other lifestyle changes one at a time. However, for best results, continue the prescribed treatment on time and without fail. If you face any problems with medications, such as allergies or side effects, then consult doctors and get your medicines replaced.
Improve your mental health
Stress, anxiety, and depression are always considered to be among the root causes of all health problems, and thyroid dysfunction is no exception. They further enhance the chances of giving you sleepless nights as well. Reduce stress or use stress busters like mindfulness, breathing exercises, listening to music, or talking to your loved ones during the day or before lying on the mattress.
Establish a sleep cycle
As we have seen, a disturbed sleep-wake cycle is responsible for causing thyroid diseases, so ensure to establish a sleep cycle. Determine a regular sleep time and adhere to it every day, including holidays and weekends. Also, set an alarm for every day and get out of the mattress as soon as you wake up, no matter how soft or best your mattress is.
Keep a consistent sleep routine
All of our habits and routines are interrelated and impact each other very deeply. Setting and sticking to a consistent bedtime routine is as important as creating and sticking to a sleep-wake schedule. Create a bedtime routine that you can follow for at least 60 minutes before sleeping on the mattress. Replace electronic devices with books and journals. Keep mobiles, and laptops away from your bed and avoid screen time to prepare your brain to release the sleep hormone melatonin. Try relaxing activities like meditation, and drinking warm milk or chamomile tea, to reduce anxiety and mood swings caused by an underactive or overactive thyroid.
Establish a healthier lifestyle
A healthier lifestyle will not only help you sleep better even if you have thyroid problems, but it will also improve your overall well-being. Start with healthy, balanced meals full of nutrients and vitamins that are necessary for better functioning of your body. Include foods with or without iodine based on the iodine level in your body. Add low-calorie foods to your diet if you are gaining extra weight due to thyroid disease.
Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bedtime. Both of these substances will keep you awake for hours. Instead, try drinking herbal tea or chamomile tea before bedtime.
Add 30 to 90 minutes of exercise to your daily routine, based on your personal stamina and capacity. Exercise has been shown to improve your overall health by helping you lose weight, reduce your risk of heart disease, and improve your blood pressure levels. Additionally, exercise can help you get a good night’s sleep by helping you rid yourself of stress hormones like cortisol. When you’re tired, cortisol causes you to have difficulty sleeping.
Make your sleeping space sleep-worthy
Like adequate sleep, where you sleep is also important. There are a few things you can do to make your sleeping space sleep-worthy. A cool, dark, and silent room is what you need for a night of better and more peaceful sleep at night. Ensure to turn off lights and close windows with thick curtains to prevent brightness. Lower the room temperature to 17 to 18 degrees with the help of fans and air conditioning. Use noise blockers to make the bedroom soundproof.
For a better sleep environment, use soothing aromas and sleeping sounds. It helps create a positive vibe in the room and also relaxes your mind, making you fall asleep slowly.
Replace your old mattress with the
Conclusion:
A considerable part of the world’s population is affected by thyroid diseases, which can have a significant influence on sleep and overall health. While there is no easy solution, the best part is that with the right diagnosis and medications, you can regain your former self, including quality sleep.





























































